Microscopy Effects on Images
Detectors:
Array Detectors
Cameras, CCD's EMCCD's Back thinned CCD's, CMOS, SCMOS
These detectors measure photons and produce electrons in each pixel. The pixels are then readout as a serial list of values representing the photon intensity at each location.
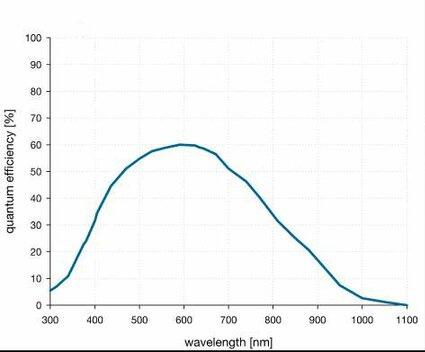
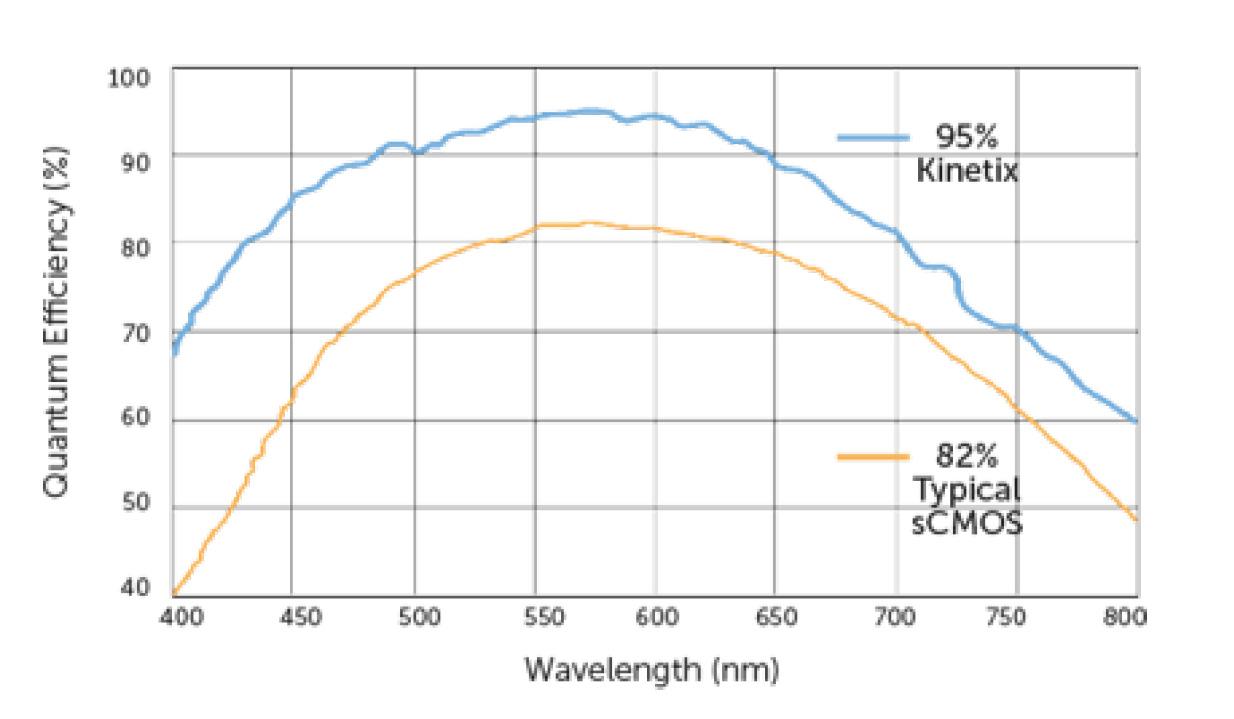
Quantum Efficiency
The quantum efficiency is a ratio between the number of photons hitting a pixel to the number of electrons in the well
|
PCO edge 5.5 sCOMS |
Kinetix sCOMS |
| IXon CCD |
Noise
- Read Noise:
- Errors in reading elections in wells. Read noise is independent of ingratiation time and effects low light level imaging.
- Shot noise:
- statistical differences in the number of photons hitting the pixel
- Dark noise:
- Is the accumulation of electrons when no photons are hitting the pixel
- Hot Pixels/ Dead Pixels:
- Pixels with Higher or lower dark noise
Pixel Size
Use magnification and Nyquist theorem
Point Detectors
PMT's APD's
Quantum Efficiency
Noise
other Info
more stuff
even more stuff
Objectives
https://www.microscopyu.com/digital-imaging/introduction-to-charge-coupled-devices-ccds